1. Introduction
Search engine optimisation (SEO) is the process of improving the visibility of a webpage in search engine results through organic (unpaid) methods. Generally, the higher a website ranks on the results page, and the more frequently it appears, the more visitors it will receive through search engines.
Modern SEO strategies not only focus on keywords and content but also take into account the following factors that essential in determining search rankings:
- user experience (UX)
- core web metrics (page load speed, interactivity, and visual stability)
- mobile-first indexing
- E-E-A-T (experience, expertise, authoritativeness, trustworthiness).
2. Good content
When search engines assess a website’s ranking, they heavily prioritise high-quality, user-friendly content. Effective content creation requires:
- Unique content: Avoid duplicate content across pages. Use canonical tags to indicate original sources if necessary.
- Each page should focus on one clear idea. Search engines and users both prefer pages that are easy to understand and relevant to a specific topic.
- Ensure content is informative yet concise, delivering value without unnecessary detail.
- Keep content updated regularly to maintain relevance.
- Incorporate various content formats, such as text, audio, video, images, PDFs, and more. Repurposing content into multiple formats can engage different audience segments.
- Long-form content (1,500 words or more) can demonstrate authority, provided it remains structured and engaging.
- Use interactive content like quizzes, polls, surveys, or infographics to boost user interaction and engagement.
- Prioritise core web metrics, especially page speed and visual stability, ensuring users do not encounter sudden layout shifts.
- Implement structured data (Schema.org) to help search engines better understand your content and improve the chances of displaying rich results.
2.1 Key content guidelines:
- Crucial information should appear:
- In the first two words of a sentence,
- In the first two sentences of each paragraph
- In the first two paragraphs on each page.
- Effective content types include:
- Blogs
- Expert interviews
- Case studies
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How-to guides
- Checklists.
- Write according to plain language principles. Content with a Flesch-Kincaid reading level of 8 (equivalent to an eighth grader) is generally preferred (see writing guidelines).
- Ensure there are no spelling or grammatical errors.
- Avoid using frames, JavaScript-heavy elements, or image-based text that may hinder search engines’ ability to access your content.
- Use a well-structured internal link architecture that directs users to key pages. The fewer clicks required to reach content from the root directory, the better for search visibility.
- Secure backlinks from authoritative websites to improve ranking, and link to credible sites from your pages as well.
- Use 301 redirects** when content is moved or removed to maintain search engine equity.
- Use descriptive names for pages, directories, and files (e.g., use "summer-sale.html" rather than "page2.html").
3. Keywords
While meta keywords are no longer widely used, keyword optimisation is still essential for crafting content that ranks well.
Conduct thorough keyword research to align with search terms used by your audience, incorporating latent semantic indexing (LSI) keywords and long-tail keywords (multi-word phrases) to reflect specific searches. With the increasing use of voice search, consider adding more conversational phrases.
3.1 Best practices for using keywords
- Include keywords in the title tag. Each page should have a unique title.
- Use SEO-friendly URLs, incorporating keywords. Hyphenated words in URLs (e.g. "budget-report-2023") are preferable to underscores, as search engines may interpret the latter as one word.
- Include keywords in the <h1> heading tag, but only use one per page. Use <h2> and <h3> tags for subheadings as needed.
- Incorporate keywords into the meta description. Although search engines may not always display it, a well-crafted description can improve click-through rates (CTR).
- Use alt tags with keywords for images.
- Ensure file names (e.g. images, PDFs) contain keyword-rich descriptions (e.g. "president-ramaphosa.jpg").
- Avoid keyword stuffing by using natural, readable placements, especially within the first 100 words.
- Use bold formatting for key phrases, but sparingly.
- Use keywords in anchor text rather than generic phrases like “click here.” Ensure links are descriptive and contextual (e.g. "read the guide on how to apply for a subsidy").
- Remember to write for users first, keeping content clear, engaging, and informative.
4. Metadata
Every webpage requires metadata to be effectively searched and categorised:
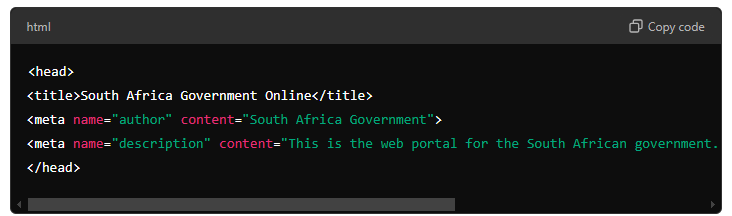
4.1 Metadata guidelines
- Ensure title tags are concise and within 60 characters.
- Write meta descriptions with a compelling call to action, keeping them within 155-160 characters.
- Implement Open Graph (OG) tags to ensure proper presentation on social media platforms.
5. On-page optimisation
With search engines increasingly prioritising mobile-first indexing, it is crucial to optimise websites for mobile users. Ensure that:
- The website has a responsive design and loads quickly across all devices.
- Image compression and next-gen formats (such as WebP) are used to enhance load times.
- Pay close attention to core web metrics, particularly visual stability, avoiding layout shifts that could disrupt the user experience.
6. User engagement signals
Search engines evaluate user engagement metrics, such as bounce rate and dwell time, as indicators of content quality. You can improve these metrics by:
- Using internal linking to relevant content, promoting a cohesive user journey through topic clusters.
- Reducing bounce rates by ensuring pages load quickly and are easy to navigate.
7. Backlinks
Backlinks from authoritative and relevant websites significantly boost SEO:
- Focus on quality backlinks over quantity.
- Regularly audit backlinks and consider disavowing any toxic backlinks that may harm your site’s reputation.
8. Technical SEO
- Use HTTPS across all webpages to improve security and rankings.
- Maintain an up-to-date XML sitemap and submit it to search engines to ensure pages are indexed.
- Regularly check for 404 errors and use 301 redirects to ensure users are redirected correctly and search equity is preserved.

